Xcode configuration files (.xcconfig) provide a powerful way to manage build settings for your iOS projects. They enable you to define and organize configurations for different build environments, such as Debug, Release, or custom setups.
Setup Xcode configuration file
To create a configuration file:
- In Xcode, right-click on your project in the file navigator and select New File from Template....
- Choose Configuration Settings File and click Next.
- Name the file (e.g.,
Parameters.xcconfig) and save it in your project directory.
Once created, you can edit the file to define build settings as key-value pairs:
BASE_URL = https:\/\/api.example.com
API_KEY = DEV_API_KEY_12345
Many value types are possible for settings, but the following table lists the most common ones:
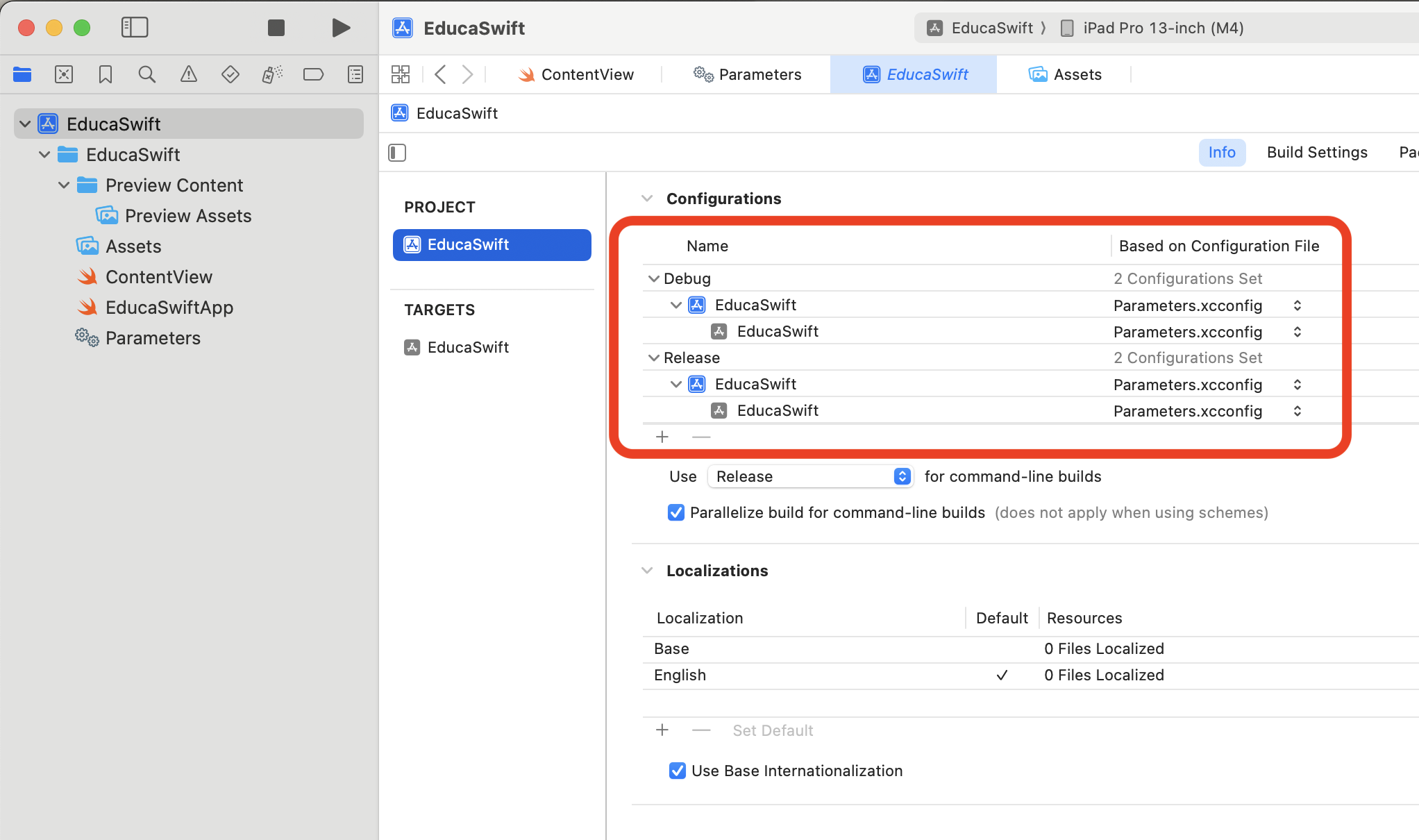
To apply the configuration file to a build environment:
- Click on your project in the file navigator and select the Info tab.
- Under Configurations, assign the appropriate
.xcconfigfile to each build configuration (e.g., Debug, Release).
This setup ensures that the settings defined in the .xcconfig files are applied during the build process.
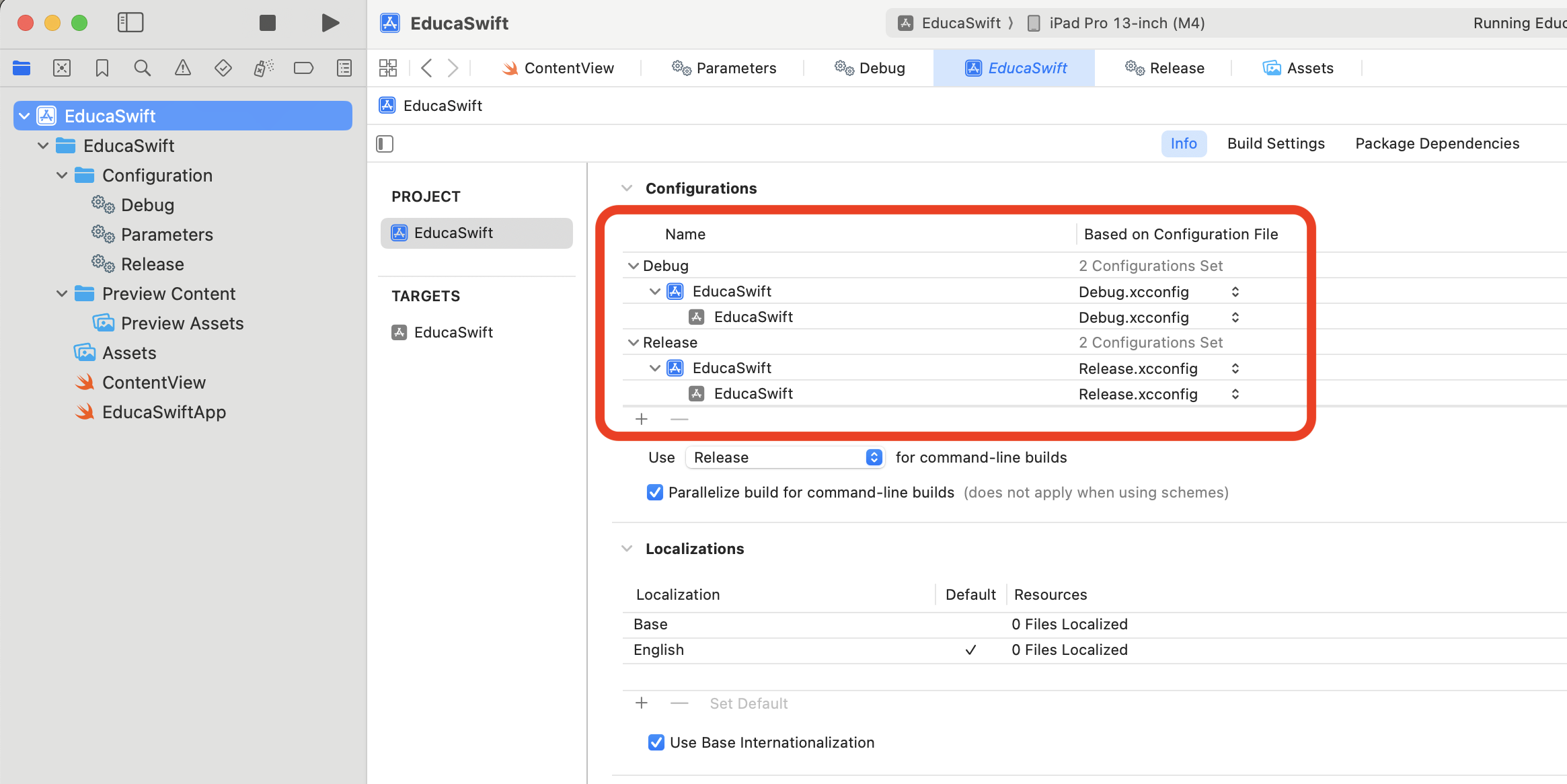
Combining files
You can structure your configuration data in different files and link them to each other. Let's see an example where we create one file per environment and both of them will include common seetings, Parameters.xcconfig in this case.
Parameters.xcconfig
BASE_URL = https:\/\/api.example.com
Debug.xcconfig
#include "Parameters.xcconfig"
API_KEY = DEV_API_KEY_12345
Release.xcconfig
#include "Parameters.xcconfig"
API_KEY = API_KEY_12345
Now we can set Release.xcconfig and Debug.xcconfig to our build environments.
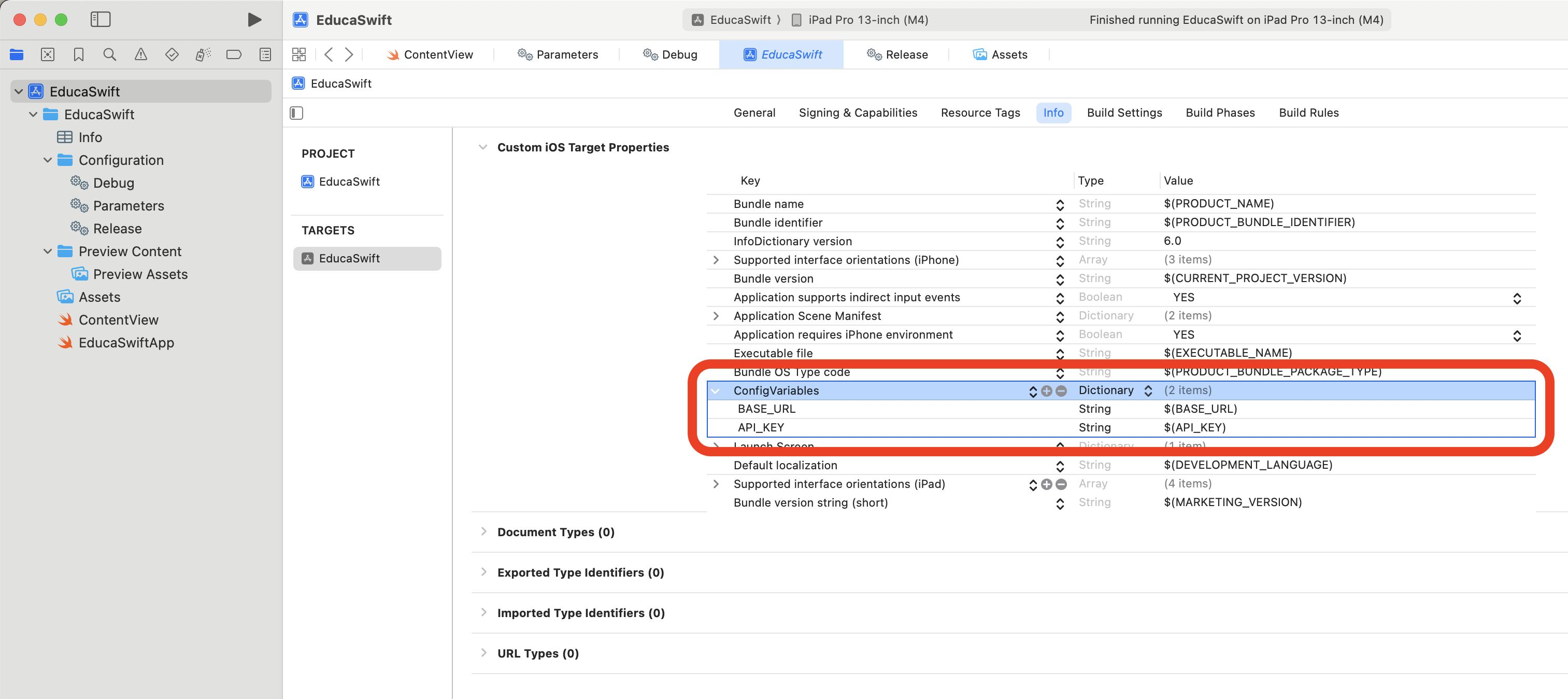
Load variables on Runtime.
We can load our configuration file variables programmatically using Bundle. In order to be able to do this, we need to include our variables to the info tab of our target. We recommend to add them as a dictionary for a better organization.
This will create an info.plist file that will contain your custom variables. You can do changes on both sides since any change in this file will update the target's info tab.
Now we are ready to load our variables.
guard let configVariables = Bundle.main.infoDictionary?["ConfigVariables"] as? [String: Any] else {
return
}
let baseUrl: String? = configVariables["BASE_URL"] as? String
let apiKey: String? = configVariables["API_KEY"] as? String
Replacing system config variables
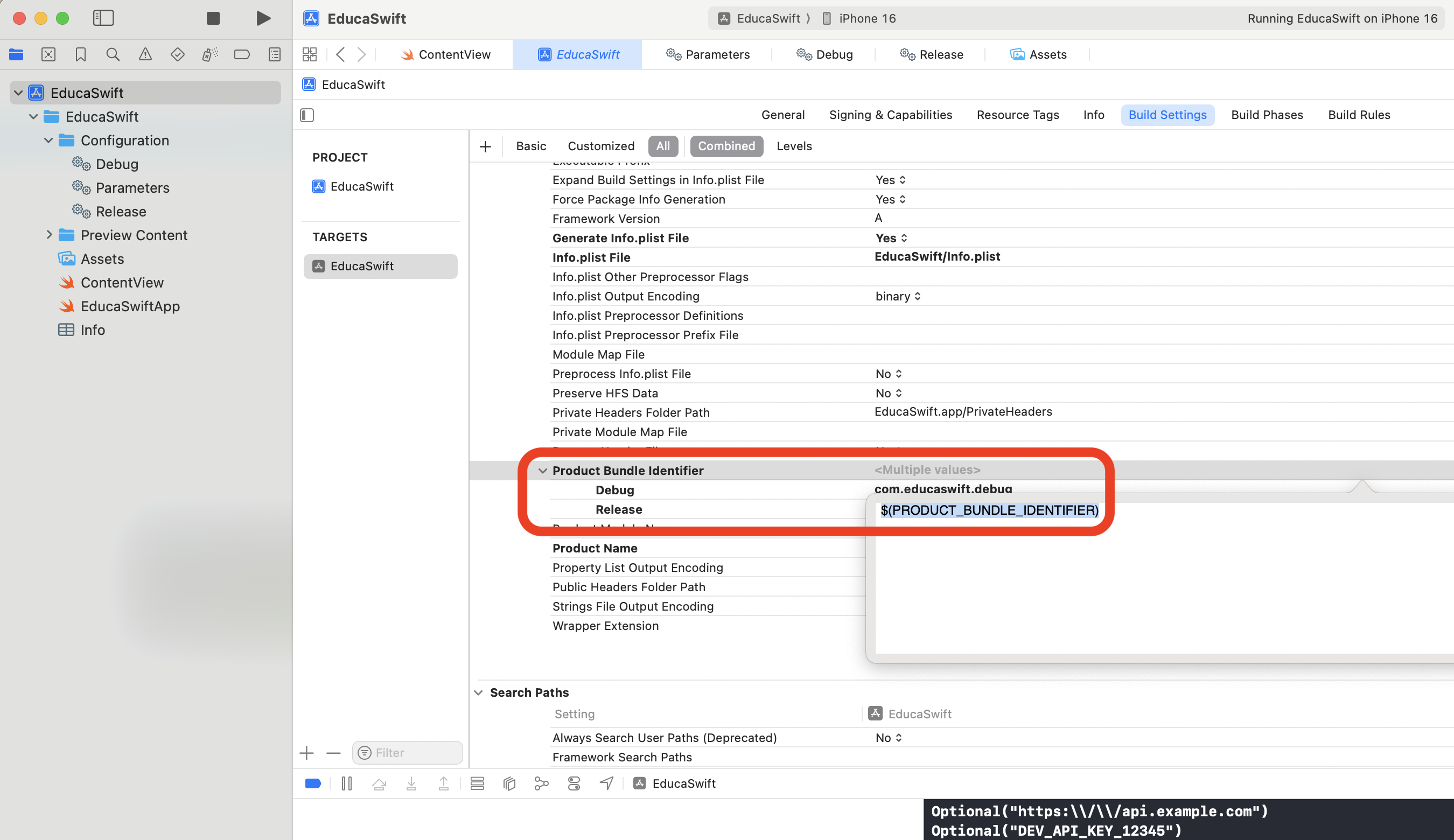
Apart from adding our own variables, we can also use variables defined by the system. Let's see an example where we add PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER to our config files.
Debug.xcconfig
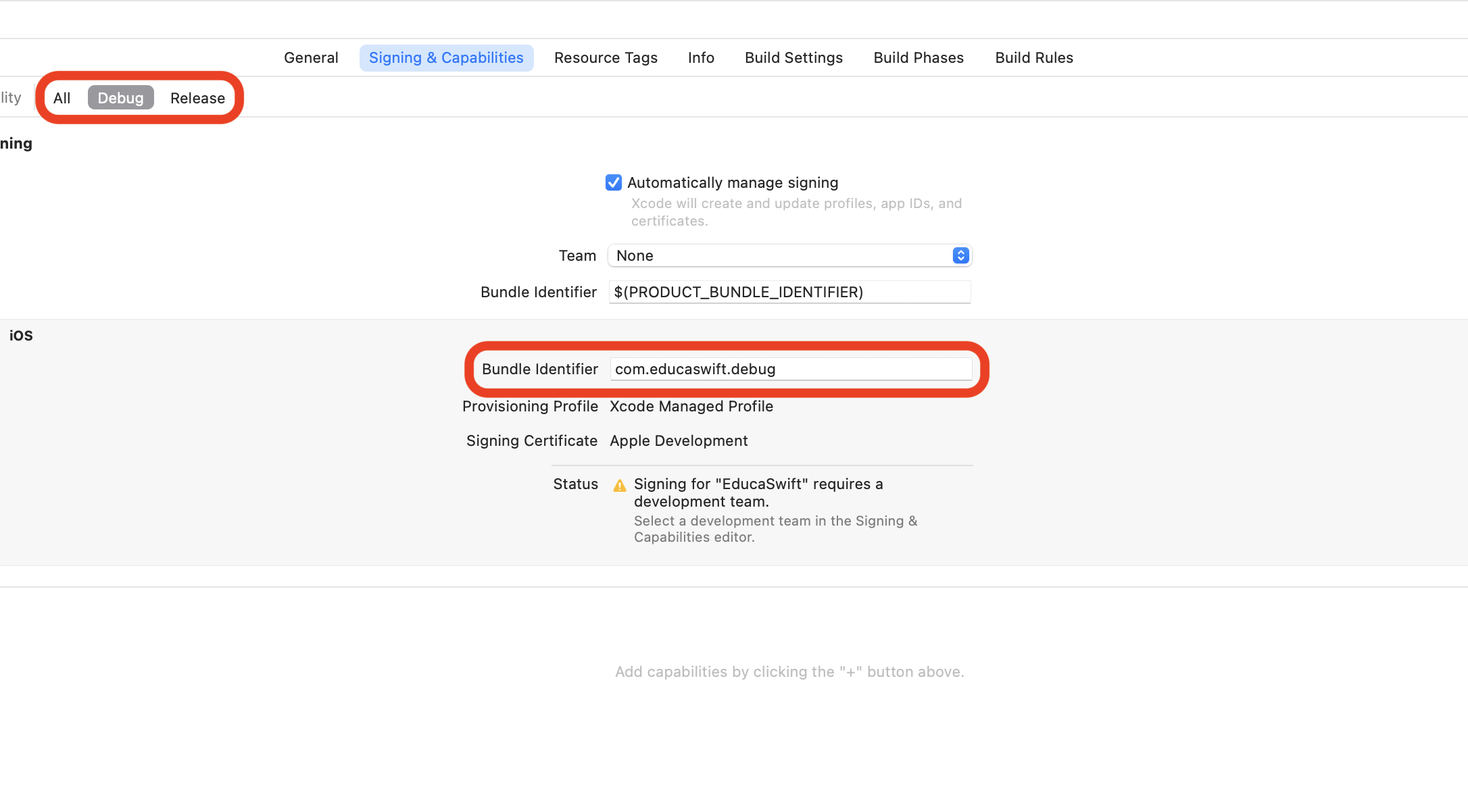
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = com.educaswift.debug
Release.xcconfig
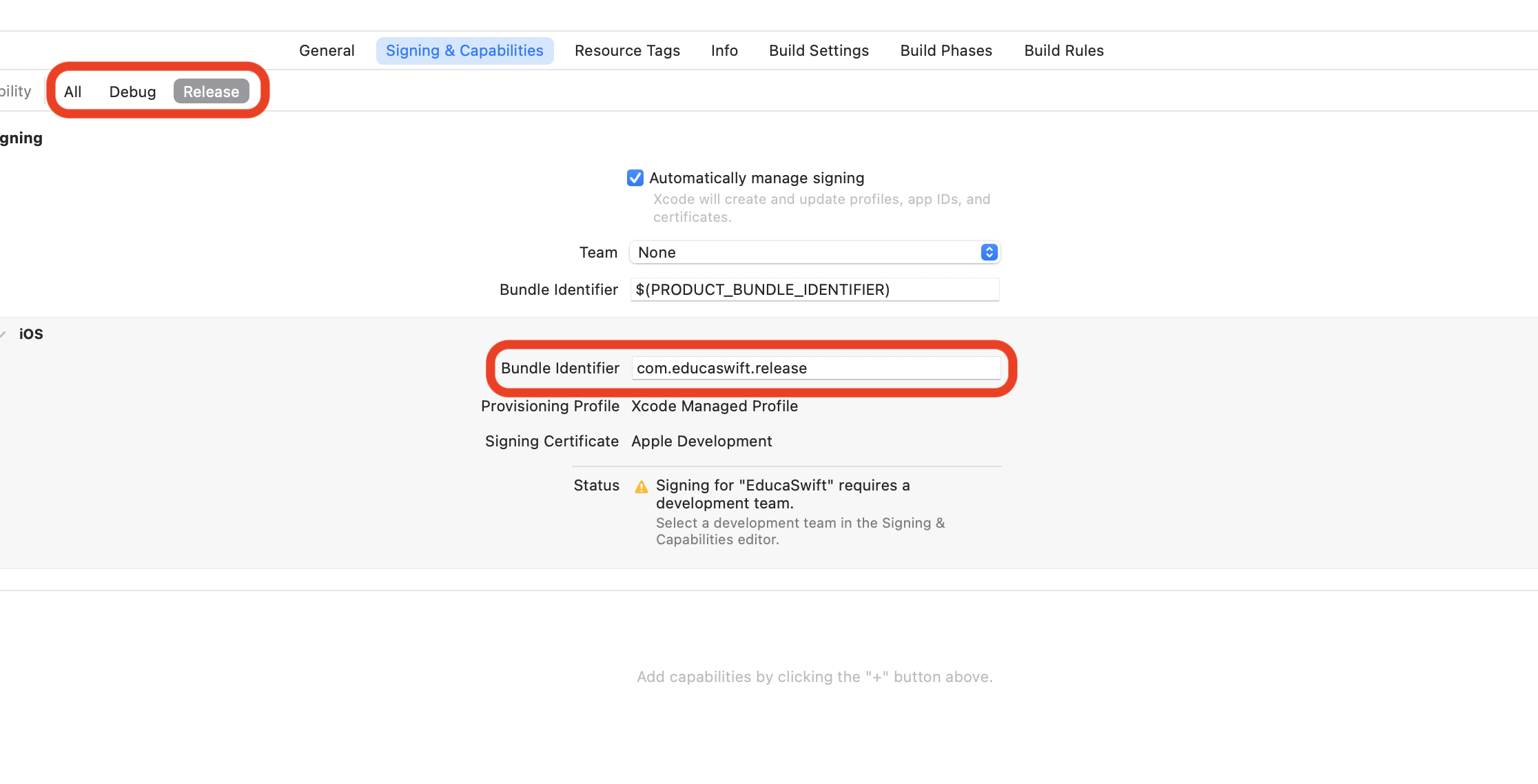
PRODUCT_BUNDLE_IDENTIFIER = com.educaswift.release
Then we can use this variable in the Build Settings tab.
As you can observe, this will update the Signing & Capabilities info.

Be the first to comment