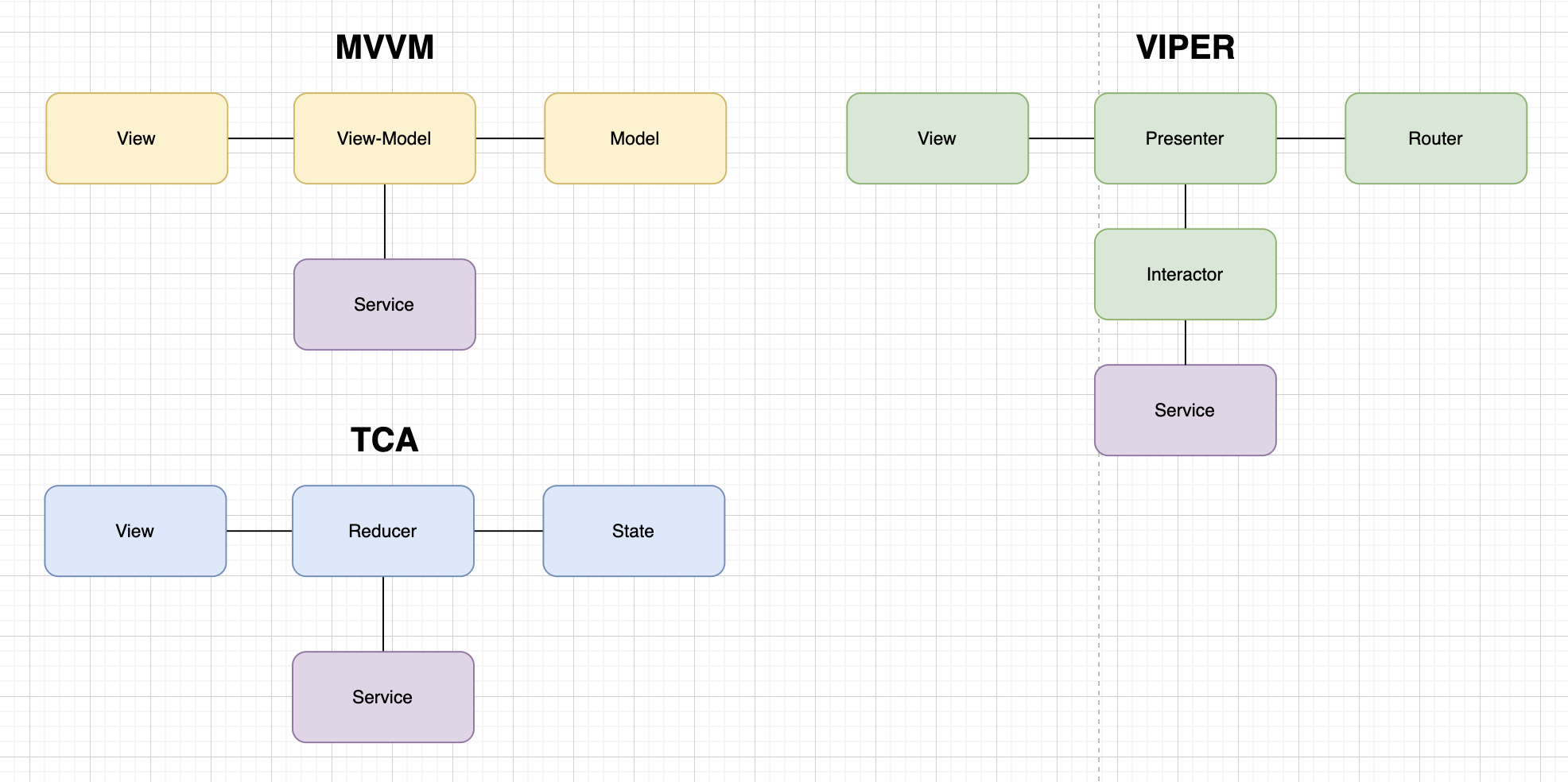
In any Swift architecture, the concept of a "Service" plays a crucial role. Services are essential for managing external data, handling networking tasks, and organizing code in a way that maintains a clean separation of concerns. In this article, we’ll explore what a service is, how it fits into different architecture, and a basic implementation of a service in Swift.
A service may handle:
- Fetching data from a remote API
- Saving data to a local database
- Processing and transforming data before sending it to the ViewModel
Benefits of Using Services
Incorporating services into your architecture provides several benefits:
- Modularity: Services keep your code organized by isolating network and data operations into separate, reusable components.
- Testability: By isolating data-fetching logic in services, you can test data handling independently from the rest of the app.
- Reusability: Services can be reused across multiple ViewModels, making them efficient and reducing code duplication.
Creating a service
Let's see an example where a ProductService provides a function to fetch a list of products. As you can see this service will manage the connection with the server and will provide a final result, so wherever you use this service, you only need to worry about calling fetchProduct function.
import Foundation
enum ProductServiceError: Error {
case wrongUrl
case networkError
}
class ProductService {
func fetchProducts() async throws -> [Product] {
guard let url = URL(string: "https://educaswift.com/public/products.json") else {
throw ProductServiceError.wrongUrl
}
do {
let urlRequest = try URLRequest(url: url, method: .post)
let (data, _) = try await URLSession.shared.data(for: urlRequest)
let products = try JSONDecoder().decode([Product].self, from: data)
return products
}
catch {
throw ProductServiceError.networkError
}
}
}
We could add more function to our service like addProduct, removeProduct, fetchProductDetail, always related with the purpose of the service, in this case, managing products.
ProductService, UserService, PostService...
ServiceError
A Service handles data from various sources, such as network requests, databases, or other systems. To streamline error handling, we've created a unified error type, ProductServiceError, so that our Service returns a consistent error type across all operations.
Using our Service
As we mentioned earlier, a Service is usefull in any architecture, but for this example let's see how it would work in a ViewModel.
@Observable
class ViewModel {
var products: [Product] = []
let productService: ProductService = ProductService()
func onAppear() {
Task {
await fetchProducts()
}
}
func fetchProducts() async {
do {
products = try await productService.fetchProducts()
}
catch {
// Handle errors here
}
}
}
Be the first to comment